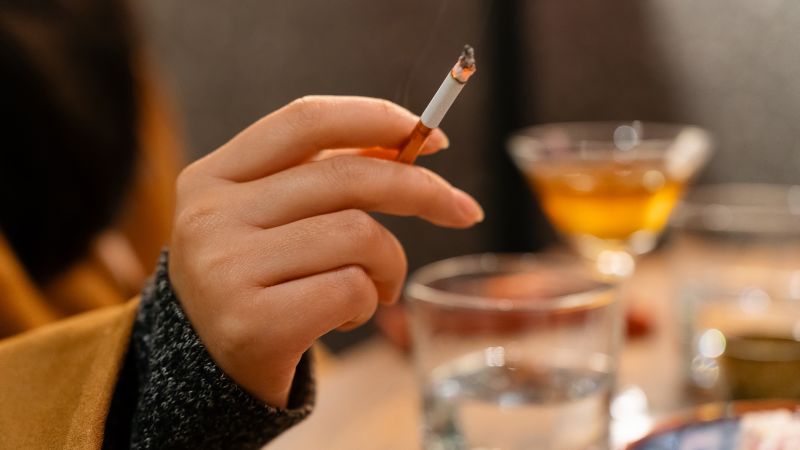
In a recent study by the American Cancer Society, it was found that about 40% of new cancer cases among adults ages 30 and older in the United States, as well as nearly half of cancer-related deaths, could be attributed to preventable risk factors.
Dr. Arif Kamal, chief patient officer with the American Cancer Society, emphasized the importance of lifestyle changes in reducing the risk of cancer. Smoking was identified as the leading risk factor, contributing to nearly 1 in 5 cancer cases and a third of cancer deaths. Other key risk factors included excess body weight, alcohol consumption, physical inactivity, diet, and infections such as HPV.
The study analyzed 18 modifiable risk factors across 30 types of cancer, revealing that these factors were linked to over 700,000 new cancer cases and more than 262,000 deaths in 2019. Dr. Kamal highlighted that DNA damage or a fuel source can lead to cancer growth, with modifiable risks playing a significant role in cancer development.
Certain cancers were found to be more preventable than others, with modifiable risk factors contributing to over half of new cases for 19 of the 30 types of cancer evaluated. In particular, modifiable risk factors were linked to at least 80% of new cases in 10 types of cancer, such as melanoma and cervical cancer.
Lung cancer had the largest number of cases attributable to modifiable risk factors, with smoking being the primary factor. Excess body weight was the second largest contributor to cancer cases, associated with a significant portion of deaths in several types of cancer.
Dr. Marcus Plescia, chief medical officer for the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, emphasized the importance of addressing core behavioral risk factors to reduce the rates and outcomes of chronic diseases like cancer. He stressed the need for policymakers and health officials to create environments conducive to healthy choices, especially in disadvantaged neighborhoods.
As rates of early-onset cancer continue to rise in the US, experts urge the adoption of healthy habits early in life. It is never too late to make lifestyle changes to reduce cancer risk, and even small adjustments can have a profound impact on overall health. By minimizing exposure to certain risk factors, individuals can actively reduce their cancer risk.