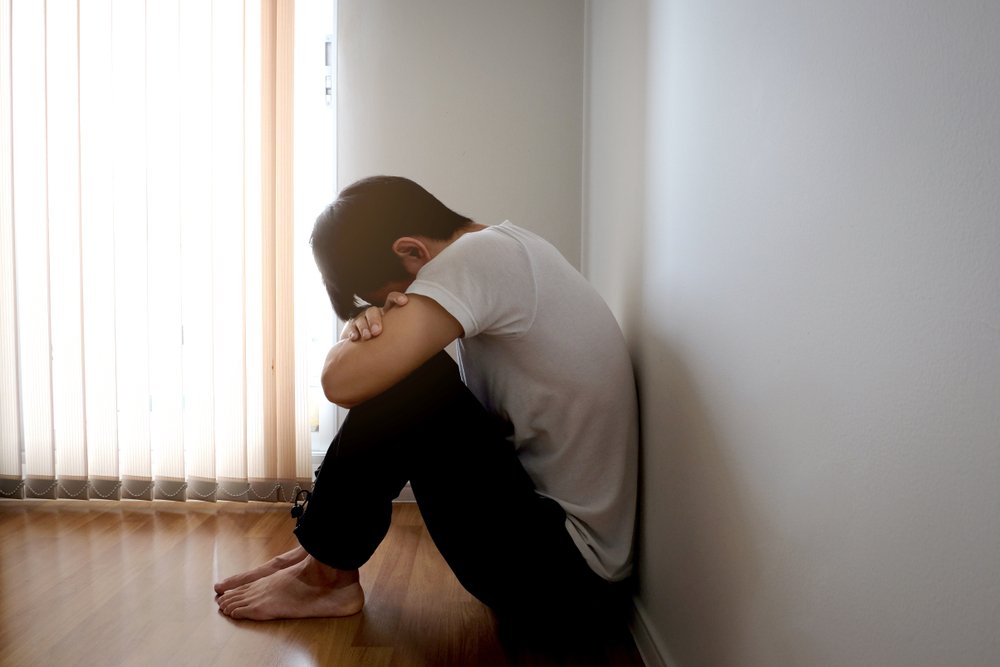
Mental health refers to the emotional, psychological, and social well-being of individuals. The increasing mental health issues worldwide pose a significant threat to individuals and societies. Understanding the scope and impact of the mental health crisis is vital for developing effective solutions to this pressing issue. Here is a detailed exploration of this important topic.
Definition of the Mental Health Crisis
The mental health crisis refers to the deterioration of individuals’ mental states, the widespread nature of this condition in society, and the resulting negative consequences at the individual, societal, and economic levels. Mental health issues encompass various conditions, including anxiety, depression, stress, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia, which significantly affect individuals’ quality of life. The crisis not only affects those diagnosed with mental health conditions but also impacts their families, workplaces, and communities.
Causes of the Mental Health Crisis
1. Impact of the Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has had profound and long-term effects on mental health worldwide. Restrictions imposed during the pandemic, social isolation, and uncertainty have negatively impacted individuals’ mental well-being. Research shows a significant increase in anxiety and depression rates following the pandemic. For example, the WHO (World Health Organization) reported a 25% rise in mental health issues during the early months of the pandemic. Many people experienced a loss of routine, fear of illness, and grief from losing loved ones, leading to a deterioration in mental health.
2. Role of Social Media
Social media has become an indispensable communication tool, but it also has negative effects. Social media platforms lead individuals to compare themselves with others, resulting in low self-esteem, anxiety, and depression. The prevalence of idealized representations of life online can create unrealistic expectations. Especially among young people, cyberbullying and online pressure have increasingly contributed to mental health issues. Studies have shown that excessive social media use is linked to increased feelings of loneliness and decreased life satisfaction.
3. Economic Challenges
Economic uncertainties, job loss, poverty, and financial stress are significant factors negatively affecting mental health. Economic crises can trigger anxiety and depression in individuals. Low-income individuals and families are particularly sensitive to such stress factors. Research shows that rising unemployment rates have a direct impact on mental health issues. Furthermore, economic disparities can exacerbate feelings of hopelessness, leading to a cycle of poverty and poor mental health.
4. Educational and Workload Pressures
Increasing educational and workload pressures trigger mental health problems among both young people and adults. Competitive educational systems and workplace stress elevate individuals’ stress levels, leading to burnout. For instance, a study among university students found that over 40% reported academic pressure negatively affecting their mental health. In workplaces, unrealistic expectations and a lack of work-life balance can lead to chronic stress and mental fatigue, contributing to the overall mental health crisis.
5. Societal and Cultural Factors
The cultural structures of societies significantly influence mental health. In some societies, stigma and prejudice against mental health issues can hinder individuals’ willingness to seek help. This situation reduces access to mental health services, deepening the problems. For example, negative attitudes towards mental health issues in developing countries can prevent individuals from seeking treatment. Cultural beliefs about mental health can also impact how individuals perceive their own mental struggles, often leading to denial or shame.
6. Biological Factors
Biological factors such as genetic predisposition, hormone levels, and imbalances in brain chemicals also play a crucial role in the development of mental health issues. For instance, individuals with a family history of mental health problems are at a higher risk of encountering similar issues. Neurotransmitter imbalances, such as those involving serotonin and dopamine, can lead to mood disorders. Additionally, hormonal changes, especially during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can influence mental health.
7. Environmental Stressors
Environmental stressors, such as natural disasters, violence, and community instability, can also contribute to mental health crises. Individuals living in high-crime areas or those who have experienced trauma are at greater risk for developing mental health issues. The impact of climate change, leading to natural disasters, displacements, and food insecurity, can exacerbate mental health challenges, especially in vulnerable populations.
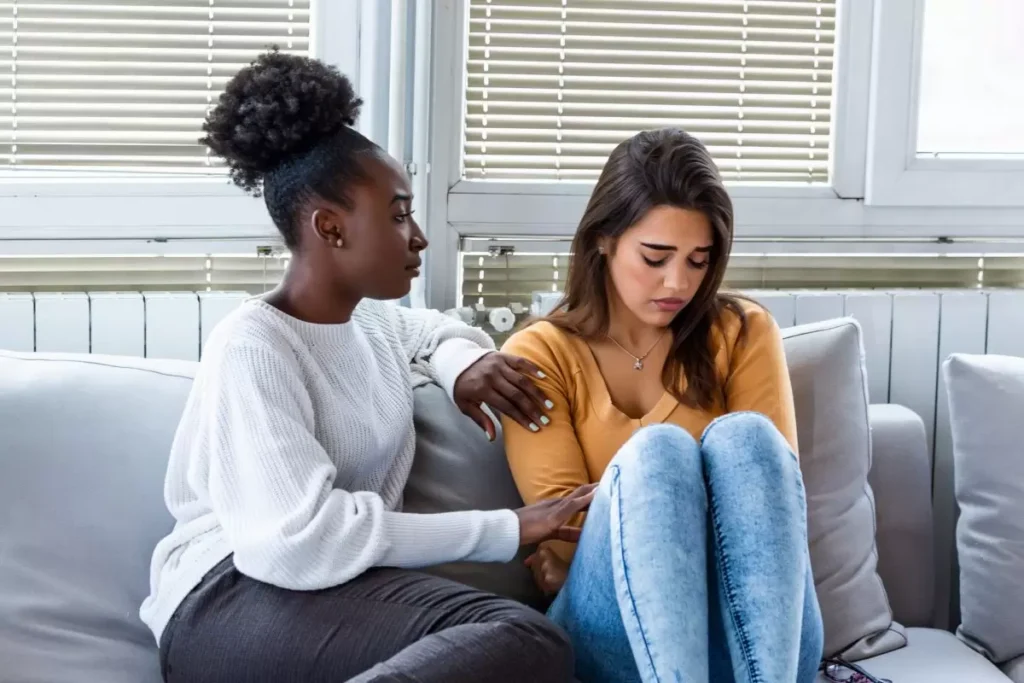

Consequences of the Mental Health Crisis
1. Individual Effects
Mental health issues significantly affect individuals’ quality of life. Conditions such as anxiety, depression, loneliness, and burnout negatively influence daily activities and weaken social relationships. As a result, individuals may experience feelings of isolation and withdraw from social activities. This can lead to a vicious cycle where social withdrawal exacerbates mental health issues, making recovery more difficult.
2. Societal Effects
Mental health issues pose a threat to overall societal health. Job loss, increased healthcare costs, and social discord can lead to societal unrest. The rise in the number of individuals with mental health problems can negatively impact a society’s economic and social development. Families may face economic strain due to the inability of affected members to work, leading to a broader impact on community resources and support systems.
3. Pressure on Healthcare Systems
The rise in mental health issues places immense pressure on healthcare systems. While the demand for mental health services increases, the provision of these services often remains inadequate. Shortages of specialists, long waiting times, and high costs prevent individuals from receiving the support they need. Mental health services often lack funding and resources, leading to a cycle of neglect that perpetuates the crisis.
4. Burnout Syndrome
Mental health issues can trigger burnout syndrome, especially in workplaces. Overloading employees, job dissatisfaction, and stress can lead to feelings of exhaustion, reducing productivity. This situation negatively affects workforce efficiency and creates overall dissatisfaction in the workplace. Burnout not only affects individual employees but can also lead to increased turnover rates and reduced morale within organizations.
5. Impact on Relationships
Mental health issues can strain relationships with family, friends, and colleagues. Individuals experiencing mental health challenges may struggle to communicate their feelings, leading to misunderstandings and conflict. The stress of caring for a loved one with mental health issues can also take a toll on family dynamics, often resulting in caregiver burnout.
Solution Proposals
1. Education and Awareness
Education and awareness about mental health should be increased. Informative programs about the importance of mental health should be organized in schools, workplaces, and the broader community. Workshops and seminars can help individuals become more aware of how to protect their mental health. Campaigns to reduce stigma and promote understanding can also encourage individuals to seek help when needed.
2. Accessibility
Facilitating access to mental health services is crucial. Governments should increase their budgets for healthcare services, expand the number of mental health professionals, and make mental health services more accessible. Additionally, digital health services, such as telepsychology, can simplify access to mental health support. Community health programs can also bridge gaps in care for underserved populations.
3. Community Support Programs
Community support programs play an essential role in protecting and supporting individuals’ mental health. Local communities, volunteer organizations, and families should collaborate to provide assistance to individuals. These programs can enhance social connections and positively impact mental well-being. Support groups, peer counseling, and community-based mental health initiatives can create a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation.
4. Use of Technology
Digital health applications can help individuals monitor their mental health and seek support when needed. Such applications are particularly popular among young people and can facilitate access to mental health services. Online counseling services can provide effective solutions for individuals seeking psychological support. Moreover, mental health apps that promote mindfulness, stress management, and emotional regulation can empower individuals to take charge of their mental well-being.
5. Supportive Work Environments
Workplaces should develop policies to protect employees’ mental health. Employers can implement flexible working hours, stress management training, and mental health support programs to prevent mental health issues from arising. Creating a culture of open communication and support can also help employees feel comfortable discussing their mental health needs and seeking help when necessary.
6. Public Policies and Support
Governments should create public policies aimed at protecting and promoting mental health. Increasing budgets for mental health services, strengthening healthcare systems, and conducting educational campaigns are crucial in combating mental health issues. Policies that address social determinants of health, such as housing stability, employment opportunities, and access to healthcare, can have a significant impact on mental well-being.
7. Research and Innovation
Investing in research on mental health can lead to innovative solutions and treatments. Understanding the complexities of mental health conditions, including their biological, psychological, and social aspects, can improve treatment approaches. Collaborative efforts among researchers, healthcare providers, and policymakers can foster the development of effective interventions tailored to specific populations and communities.
The mental health crisis is a global issue that requires serious attention. Its causes are diverse, and its effects span from individuals to society at large. Protecting and improving mental health is a collective responsibility that falls on every segment of society. Education, awareness, and accessible healthcare services are critical to resolving this crisis. A healthy society is only possible through the protection of individuals’ mental health. Mental health is vital not just for individuals but for the health of entire communities.
Therefore, addressing mental health issues and developing solutions is our shared responsibility. By fostering a culture of understanding, reducing stigma, and increasing access to care, we can work towards a future where mental health is prioritized, and individuals receive the support they need to thrive. Together, we can build resilient communities that promote well-being and address the challenges posed by the mental health crisis.