—
### Exploring the World’s Largest Heat Pumps
In the realm of energy innovation, an exciting development is unfolding in Mannheim, Germany. The city is set to host the world’s most powerful heat pump systems, an initiative launched by MVV Energie, an energy company committed to implementing sustainable technologies. This significant undertaking is poised to revolutionize how heat is generated, distributed, and consumed, benefiting thousands of households while contributing to decarbonization efforts.
#### The Project Overview
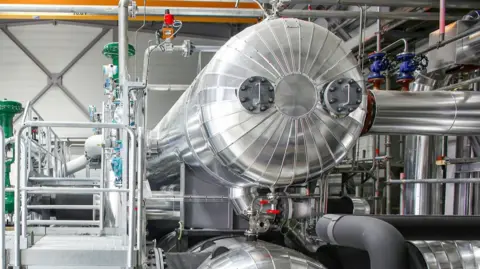
Project manager Felix Hack from MVV Environment explains that the project involves constructing heat pumps with a staggering capacity of 82.5 megawatts each, totaling a potential output of 165 megawatts for the entire system. This scale is substantial enough to cater to approximately 40,000 homes through a district heating system. Importantly, these heat pumps will extract warmth from the nearby River Rhine—fixated as one of the most extensive water-sourced heating mechanisms ever designed.
The ambition doesn’t stop at sheer capacity. MVV plans to utilize a remarkable two-meter diameter pipe that is large enough for someone to walk through upright. “We plan to take 10,000 liters of water per second,” Hack asserts, highlighting the sheer scale of infrastructure required. Once the water extract and heat are obtained, it will be returned to the river, thus maintaining environmental regulations and minimizing ecological harm.
#### Environmental Impact
Heat pumps operate by absorbing thermal energy from their surroundings—a concept that distinguishes them from traditional heating methods. By harnessing warm air, ground heat, or body water, these systems transfer energy with a principle that utilizes refrigerants to amplify heat temperatures effectively. This technology remains pivotal as cities aim to pursue less carbon-intensive energy sources.
As Hack notes, transitioning away from coal at the Mannheim plant—a historic relic of fossil fuel energy—is critical for aligning with modern environmental standards. The site benefits from existing electrical grids and proximity to district heating networks, making it an ideal candidate for heat pump installations.
#### Competitive Landscape
The landscape for heat pump technology is evolving rapidly, with companies such as Everllence (formerly MAN Energy Solutions) emerging as significant players. Alexandre de Rougemont, representing Everllence, openly acknowledges that competition is present. Everllence is developing a system in Aalborg, Denmark, that will surpass the capacity of MVV’s Mannheim project, with an anticipated output of 176 megawatts earmarked for 2027.
#### Financial Considerations
Investing in such infrastructure is anything but trivial. The entire heat pump installation in Mannheim is projected to cost around €200 million (approximately $2.3 million or £176 million). As de Rougemont articulates, the basic cost of heat pump technology is estimated at €500,000 for each megawatt of installed capacity, not factoring in the associated building costs and infrastructure—highlighting the considerable financial commitment required to spearhead this energy revolution.
#### Expanding Horizons
Globally, the drive to utilize heat pumps is gaining popularity. Cities are exploring the integration of heat pumps into extensive district heating networks, in a bid to foster more sustainable energy solutions. In addition to the projects in Germany and Denmark, municipalities from Helsinki, Finland, to various parts of the UK are reimagining their heating frameworks. For instance, in Helsinki, substantial changes are underway, where heat pumps and biomass burners are increasingly favored to connect nearly 90% of buildings to an expansive 1,400-kilometer heating network.
#### Conclusion
This exciting terrain of heat pump technology underscores a decisive shift towards greener energy solutions and models for local energy consumption. As urban areas aim to reshape their heating infrastructure, the projects in Mannheim and Aalborg stand as beacons of innovation. With significant financial investments and ambitious engineering feats supporting this transformation, the global movement toward efficient and sustainable heating illustrates the potential for cutting-edge technology to harness natural resources, ultimately enhancing our collective efforts toward sustainability.
—
This elaboration provides an in-depth look at the prominent projects in Germany and Denmark while exploring the broader implications of heat pump technology internationally.